As I sit in my workshop, surrounded by the remnants of my latest RC aircraft project, I often find myself pondering the age-old debate between solid rocket boosters vs liquid fuel engines. It’s a dilemma that has sparked intense discussion among engineers and space enthusiasts alike, with each side presenting compelling arguments. Having spent years designing aircraft, I’ve had my fair share of experiences with both types of propulsion systems, and I’ve come to realize that the choice between them is not always clear-cut.
In this article, I promise to cut through the hype and provide you with a no-nonsense analysis of the trade-offs between solid rocket boosters and liquid fuel engines. I’ll draw from my own experiences as an aerospace engineer to explain the key differences between these two propulsion systems, and help you understand the implications of each choice. My goal is to empower you with a deeper understanding of the science behind these systems, so you can make informed decisions and appreciate the incredible feats of engineering that go into launching rockets into space.
Table of Contents
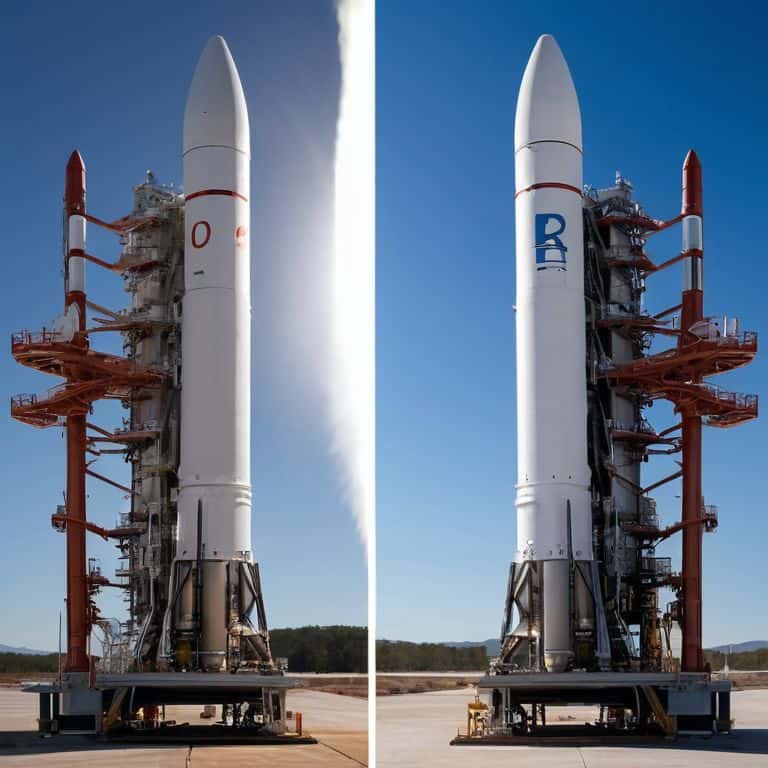
Solid Rocket Boosters
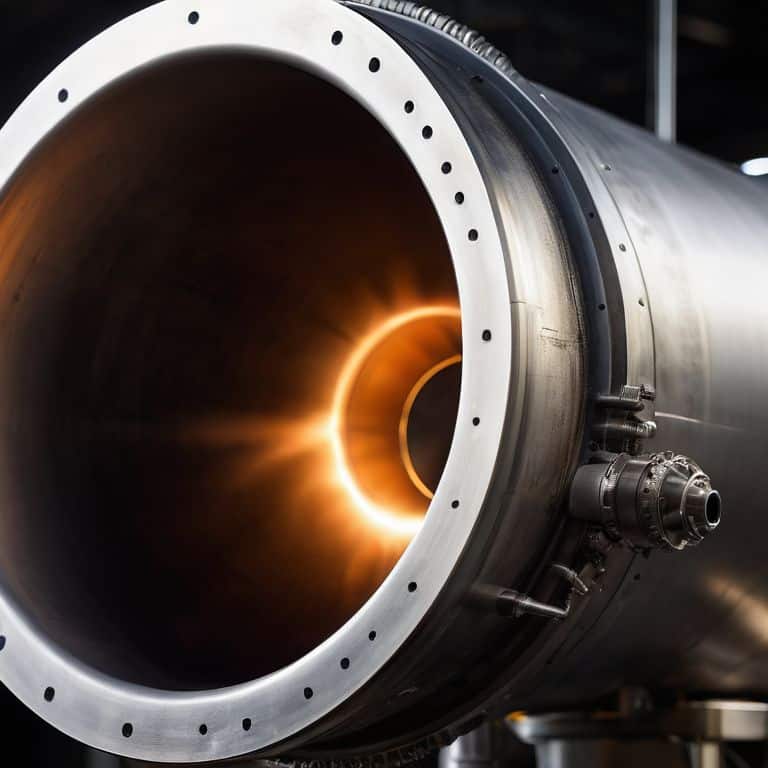

A solid rocket booster is a type of rocket engine that uses a solid fuel and oxidizer to produce thrust, with its core mechanism relying on the combustion of these solid propellants to generate a high-pressure and high-temperature gas that is expelled through a nozzle to produce a high-speed exhaust. The main selling point of solid rocket boosters is their simplicity and reliability, as they have fewer moving parts compared to liquid fuel engines, which makes them less prone to mechanical failures. Solid rocket boosters are also known for their high thrust-to-weight ratio, which allows them to provide a significant amount of thrust while being relatively lightweight.
As an aerospace engineer, I can attest that solid rocket boosters play a crucial role in many space missions, particularly during the initial launch phase. The high thrust output of solid rocket boosters allows them to overcome the gravitational forces holding the rocket on the ground, making them essential for lifting heavy payloads into space. I recall watching a rocket launch and being amazed by the sheer power and efficiency of the solid rocket boosters as they propelled the rocket into the sky, leaving a trail of flames and smoke in their wake.
Liquid Fuel Engines
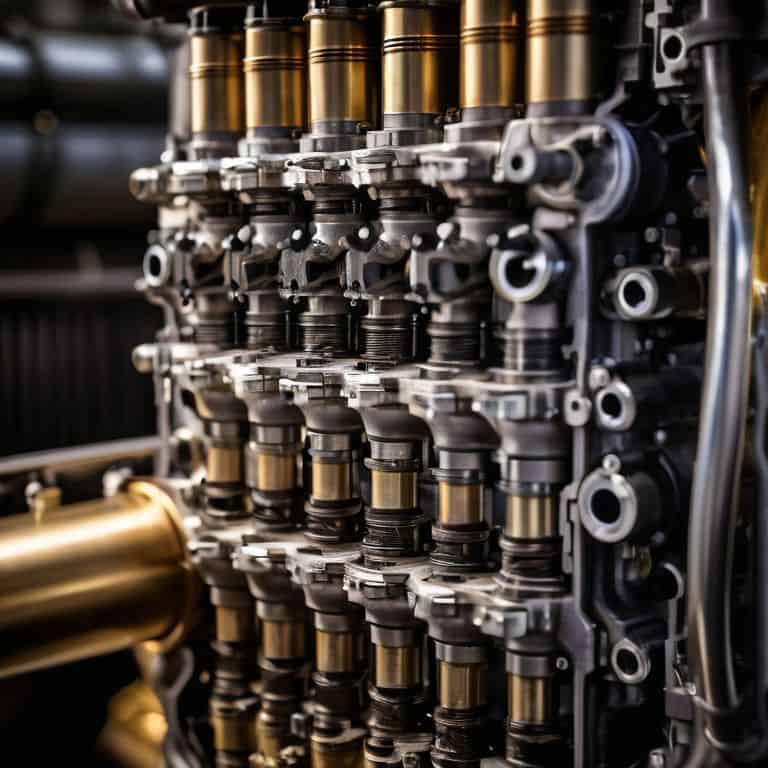

A liquid fuel engine is a type of rocket engine that uses liquid propellants, such as liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen, to produce thrust, with its core mechanism involving the combustion of these liquid propellants in a combustion chamber to generate a high-pressure and high-temperature gas. The main advantage of liquid fuel engines is their high specific impulse, which measures the efficiency of a rocket engine, allowing them to achieve a higher fuel efficiency compared to solid rocket boosters. Liquid fuel engines are also more flexible, as they can be throttled back or turned off and restarted, making them suitable for a wide range of space missions.
As someone who has worked on designing aircraft, I appreciate the complexity and versatility of liquid fuel engines, which require a deep understanding of fluid dynamics and thermodynamics to optimize their performance. I have always been fascinated by the way liquid fuel engines can be fine-tuned to achieve the perfect balance between thrust and fuel efficiency, making them a crucial component of many spacecraft. Whether it’s a launch vehicle or an orbital spacecraft, liquid fuel engines play a vital role in ensuring the success of space missions, and their advanced technology continues to evolve and improve with each new generation of engines.
Head-to-Head Comparison: Solid Rocket Boosters vs Liquid Fuel Engines
| Feature | Solid Rocket Boosters | Liquid Fuel Engines |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Higher | Lower |
| Key Feature | Simple, reliable design | High specific impulse, controllable thrust |
| Best For | Short, high-thrust missions | Long-duration, variable-thrust missions |
| Thrust Control | Limited | Highly controllable |
| Specific Impulse | Lower (around 200-250 seconds) | Higher (up to 450 seconds or more) |
| Development and Operation Complexity | Less complex | More complex |
| Environmental Impact | Higher emissions during launch | Lower emissions, more efficient |
Rocket Rivals Solid vs Liquid

As we delve into the solid rocket boosters vs liquid fuel engines debate, it’s crucial to examine the criterion of “Rocket Rivals: Solid vs Liquid” because it directly impacts the overall performance and efficiency of a launch vehicle. The choice between solid rocket boosters and liquid fuel engines is pivotal in determining the success of a space mission.
In a head-to-head analysis, solid rocket boosters offer a significant advantage in terms of simplicity and reliability. They are less prone to mechanical failures and require less maintenance, making them a more attractive option for certain types of missions. On the other hand, liquid fuel engines provide greater control over the thrust vector, allowing for more precise maneuvers and adjustments during flight.
When it comes to practical implications, liquid fuel engines have a clear edge in terms of flexibility and adaptability. They can be throttled back or shut down and restarted as needed, giving mission controllers more options in case of an emergency. In conclusion, for the criterion of “Rocket Rivals: Solid vs Liquid”, liquid fuel engines are the clear winner due to their superior flexibility and control.
Key Takeaways: Solid Rocket Boosters vs Liquid Fuel Engines
Solid rocket boosters offer simplicity, reliability, and high thrust-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for launch vehicle first stages and strap-on boosters, but are limited by their fixed thrust and inability to be throttled or shut down once ignited
Liquid fuel engines provide higher specific impulse, or efficiency, and can be throttled or shut down, but are more complex and require more maintenance, making them suitable for upper stages and main engines of launch vehicles
The choice between solid rocket boosters and liquid fuel engines depends on the specific mission requirements, including payload capacity, launch window, and desired level of control, highlighting the importance of a nuanced understanding of both technologies in rocket design and operation
The Heart of the Matter
The choice between solid rocket boosters and liquid fuel engines isn’t just about performance or efficiency – it’s about understanding the delicate dance between power, precision, and practicality, where the most elegant solution often lies at the intersection of these competing demands.
Simon Foster
The Final Verdict: Which Should You Choose?
As we conclude our comparison of solid rocket boosters and liquid fuel engines, it’s clear that each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The trade-offs between reliability and efficiency are significant, and the choice between these two ultimately depends on the specific mission requirements. Solid rocket boosters offer a high degree of simplicity and reliability, making them ideal for certain applications, while liquid fuel engines provide a higher specific impulse, resulting in more efficient use of fuel. By considering these factors, we can make an informed decision about which type of engine is best suited for a particular task.
In the end, the overall winner is the liquid fuel engine, due to its superior efficiency and flexibility. However, this doesn’t mean that solid rocket boosters are obsolete. They are still the best choice for users who prioritize ease of use and reliability, such as those involved in smaller-scale operations or with limited resources. On the other hand, liquid fuel engines are better suited for users who require high-performance and efficiency, such as those involved in large-scale space exploration or commercial launches. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each, we can make informed decisions and choose the best engine for our specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key differences in terms of thrust and efficiency between solid rocket boosters and liquid fuel engines?
When it comes to thrust and efficiency, solid rocket boosters offer a high thrust-to-weight ratio, but their efficiency is limited by their fixed burn rate. Liquid fuel engines, on the other hand, can achieve higher specific impulse, or efficiency, and can be throttled back to conserve fuel, making them more versatile for longer missions.
How do solid rocket boosters and liquid fuel engines compare in terms of cost, reliability, and maintenance requirements?
When it comes to cost, reliability, and maintenance, solid rocket boosters generally offer lower upfront costs and higher reliability due to their simplicity, but liquid fuel engines provide more flexibility and potential for reuse, which can offset their higher initial costs and maintenance needs over time.
Can solid rocket boosters and liquid fuel engines be used in combination, and if so, what are the benefits and challenges of such a hybrid approach?
Absolutely, combining solid rocket boosters with liquid fuel engines is a common practice, known as a hybrid or dual-propulsion system. This approach offers benefits like increased payload capacity and improved efficiency, but also presents challenges such as added complexity and higher development costs. I’ve seen this hybrid design used in several launch vehicles, and it’s fascinating to explore the trade-offs involved.